Normal leg and foot shapes
 If you are concerned that your child has issues with their walking, or you are worried about the shape of their legs and they are under 5 years old (please see below) then please do not see your GP for a referral to physiotherapy. Please attend one of our drop-in sessions called ‘Little Feet Physio’, these are accessible to all children who are registered with a GP in Islington only. These take place at children’s centres across Islington. Be sure to call the children’s centre before attending with your child. Further information about Little Feet drop in sessions can be found here.
If you are concerned that your child has issues with their walking, or you are worried about the shape of their legs and they are under 5 years old (please see below) then please do not see your GP for a referral to physiotherapy. Please attend one of our drop-in sessions called ‘Little Feet Physio’, these are accessible to all children who are registered with a GP in Islington only. These take place at children’s centres across Islington. Be sure to call the children’s centre before attending with your child. Further information about Little Feet drop in sessions can be found here.
In-toeing
 In-toeing gait (walking with feet turning facing inwards) is normal in children whose gait is still developing. It often resolves over time and therefore it is important that the child has a well-established gait (e.g. they have been walking independently for at least six months) before assessment.
In-toeing gait (walking with feet turning facing inwards) is normal in children whose gait is still developing. It often resolves over time and therefore it is important that the child has a well-established gait (e.g. they have been walking independently for at least six months) before assessment. In-toeing can often be associated with ‘W’ sitting (see image). If your child in-toes and often sits in a prolonged ‘W’ position, encourage your child to sit either cross legged or in a side sitting position instead.
In-toeing can often be associated with ‘W’ sitting (see image). If your child in-toes and often sits in a prolonged ‘W’ position, encourage your child to sit either cross legged or in a side sitting position instead.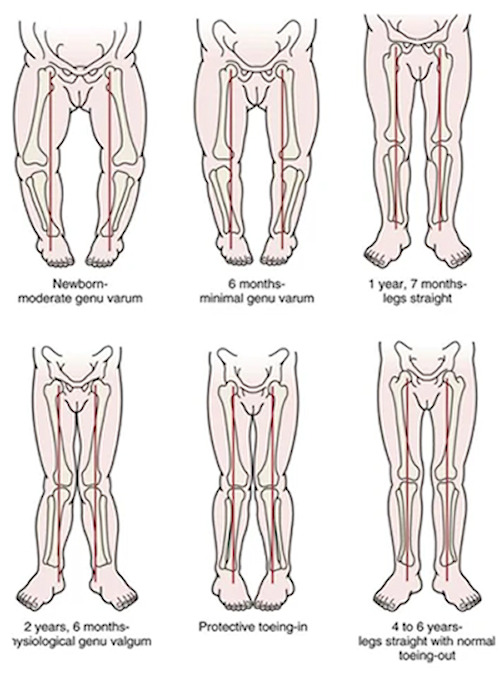
Referral to physiotherapy not necessary if:
- Symmetrical in-toeing without symptoms in children under 8.
- Full range of movement of joints. No structural tightness.
See your GP for a referral if:
- The child shows signs of abnormal neurology e.g. abnormal tone (Referral to Paediatrician also indicated in this case).
- In-toeing gait occurring past the age of 8.
- Asymmetrical in-toeing gait.
Physiotherapy exercises
Visit our web page on physiotherapy exercises for in-toeing to see suggestions for exercises you can try with your child at home. You can also download this information as a pdf if it would be helpful to be able to print it for reference.
Be aware that physiotherapy cannot prevent the tripping often associated with in-toeing.
For more information on in-toeing gait please visit the Association of Paediatric Chartered Physiotherapists page on in-toeing gait, or click here for their helpful leaflet.

Out-toeing
This is also a normal variant, although less common than in-toeing, and should also be assessed when walking is well-established (e.g. independent walking for at least six months). It is often associated with knock knees and flat feet. Although usually normal, further investigation may be warranted if the child experiences pain in their lower limbs or if their gait is asymmetrical.
See your GP for a referral if:
- Symmetrical out toeing associated with pain in lower limbs.
- Asymmetrical out-toeing gait

Bow-legs (Genu Varum)
Genu varum is a normal variant up to the age of two and will normally change to valgus by the age of four. It can be associated with overweight babies/toddlers and early walkers.
A Physiotherapy referral is not necessary.
Knock-knees (Genu Valgum)
Knock knees is a normal variant for children aged two to four years of age and tends to revert to adult alignment by six to eight years of age.
A Physiotherapy referral is not necessary.
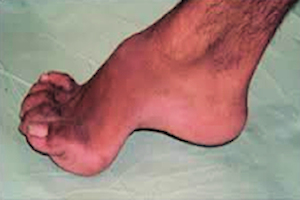
High Arch Foot (Pes Cavus)
This is where the arch of the foot is very pronounced (the opposite of a flat foot). This is rare but likely to be related to a neurological pathology. The child should therefore be screened by a Paediatrician or Orthopaedic Consultant.
A physiotherapy referral is not necessary.
Flat Feet (Pes Planus)
Flat feet is a common paediatric foot posture. It is normal in infants as the arches of the foot do not develop until 2-3 years of age and is fully formed by the time a child is 8-10 years of age.
A referral is not needed if it does not cause pain and functional issues.

Curly toes
Congenital curly toes tend to affect 3rd, 4th and 5th toes of one or both feet and tend to become more noticeable when a child starts walking. They are often flexible and result from intra-uterine moulding. They generally do not cause any gait problems. If the overriding toes are flexible/correctable, no treatment or referral is indicated.
Please attend the Little Feet physiotherapy drop-in clinic where the physiotherapist can show stretches to extend the toes if they are a little tight. This can be advised after a bath. The aim of this is to maintain or improve flexibility.
Last updated01 Apr 2025

